Table of Contents
Jaundice Newborns Symptoms Treatment
Jaundice in newborns is a common condition that can affect up to 60% of full-term babies and 80% of premature babies. It occurs when there’s a buildup of bilirubin in a baby’s blood, which leads to a yellowish tint to the skin and eyes. Although it can be worrying for new parents, jaundice is usually mild and resolves on its own. However, more severe cases need careful attention and treatment. This article will take you through the symptoms, causes, and treatments for jaundice, helping you feel more confident in caring for your little one. We’ll also share some essential products from our store to make managing jaundice at home easier and more efficient.
Jaundice in newborns is a common condition, but understanding its causes and treatment is essential for new parents. It is vital to recognize the symptoms early to ensure proper care and management. For a more in-depth understanding of jaundice and how it affects infants, refer to this comprehensive guide on newborn jaundice causes and treatments from Mayo Clinic, a trusted healthcare authority. By staying informed, you can better manage your baby’s health and well-being.
What is Jaundice in Newborns?

Jaundice occurs when the liver is unable to efficiently process and eliminate bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells break down. Newborns have an immature liver that may take some time to fully function, causing bilirubin to build up in the blood. This is what gives the baby’s skin and eyes a yellowish appearance. While mild jaundice is common and usually harmless, severe jaundice can be dangerous if not treated promptly.
For new parents, it’s important to know that jaundice doesn’t always mean something is seriously wrong. Most newborns will experience it to some degree, and with proper monitoring and care, it typically resolves without complications. Using tools like our Baby Health Monitor can help you keep an eye on your baby’s skin color and other health indicators right at home, providing peace of mind during this time.
Symptoms of Jaundice in Newborns

The primary symptom of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. This discoloration usually starts on the baby’s face and moves down the body. It’s important to regularly check your baby’s skin tone, particularly in natural light, as indoor lighting may make the yellowing harder to notice.
Additional symptoms of jaundice in newborns include:
- Poor feeding or difficulty breastfeeding
- Unusually sleepy or lethargic behavior
- Darker-than-normal urine (in contrast to the typical pale yellow of newborns)
- Pale-colored stools (especially in breastfed babies)
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to consult your pediatrician, especially if your baby seems overly tired or isn’t feeding well. Regular feedings are crucial for helping your baby’s body eliminate bilirubin naturally. Products like our Digital Baby Scale can help you track your baby’s weight and ensure they are feeding enough, as weight loss can be a sign that they aren’t eating enough to reduce bilirubin levels.
Causes of Jaundice in Newborns

There are several causes of jaundice in newborns, some of which are more common than others. The primary reason for jaundice is an immature liver that isn’t yet capable of processing bilirubin efficiently. However, other factors may contribute to the condition.
- Physiological Jaundice: This is the most common type of jaundice and occurs in most newborns as their liver matures. It typically appears 2-4 days after birth and goes away on its own within two weeks.
- Breastfeeding Jaundice: Some breastfed babies may develop jaundice if they aren’t getting enough breast milk, either due to difficulties with breastfeeding or the mother’s milk not coming in fast enough. Ensuring your baby is feeding frequently and effectively can prevent breastfeeding jaundice. If you need extra support during feedings, our Breastfeeding Pillow offers comfort for both mom and baby, making it easier to maintain frequent and longer feeding sessions.
- Blood Group Incompatibility (Rh or ABO incompatibility): When the mother’s blood type is different from the baby’s, the mother’s body may produce antibodies that attack the baby’s red blood cells, causing them to break down faster. This rapid breakdown of red blood cells leads to higher bilirubin levels.
Babies who are born prematurely are also more likely to experience jaundice because their organs are not fully developed at birth. In such cases, it’s crucial to monitor your baby’s bilirubin levels closely.
Managing Jaundice in Newborns

Managing jaundice in newborns typically involves monitoring and ensuring your baby is feeding enough to help their body naturally eliminate bilirubin. Breastfeeding or formula feeding helps promote bowel movements, which expel bilirubin from the body.
Tips for Managing Jaundice at Home:
- Frequent Feedings: Ensure your baby is eating at least 8-12 times a day. This frequent feeding will help your baby pass more stools, which helps reduce bilirubin levels.
- Sunlight Exposure: A few minutes of indirect sunlight exposure daily can help break down bilirubin in your baby’s skin. Be sure to avoid direct sunlight, as newborns are sensitive to UV rays.
- Track Weight Gain and Feeding Patterns: Monitoring your baby’s weight is essential in managing jaundice. Our Digital Baby Scale provides accurate readings, helping you ensure that your baby is gaining enough weight.
In most cases, mild jaundice will clear up on its own with these basic steps. However, if your baby’s jaundice persists or worsens, medical treatment may be necessary.
Jaundice – Management of Neonatal Jaundice
When jaundice becomes more severe, medical treatment is often required to bring bilirubin levels down. Your pediatrician will check your baby’s bilirubin levels using a blood test or a non-invasive bilirubin meter.
Medical Treatments Include:
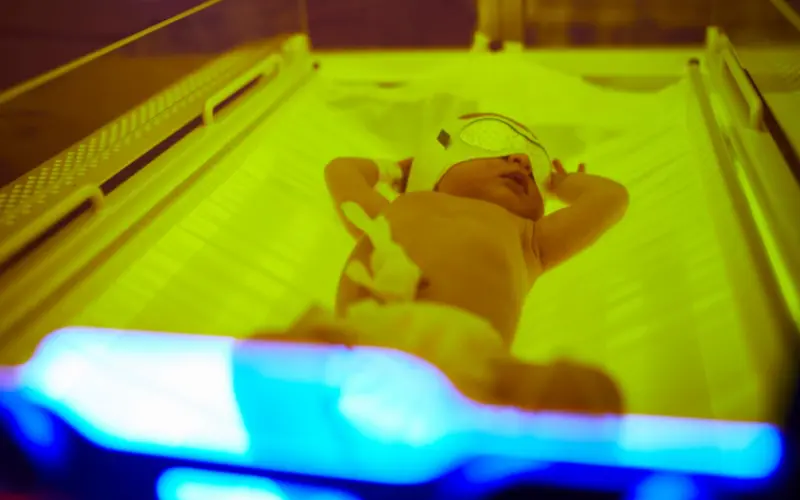
- Phototherapy: This is the most common treatment for severe jaundice. Your baby will be placed under special blue lights that help break down bilirubin in the skin. In some cases, your pediatrician may provide you with a phototherapy unit to use at home. During phototherapy, it’s essential to keep your baby hydrated by feeding them frequently.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIg): For babies with blood type incompatibility, IVIg may be given to reduce bilirubin levels by decreasing the need for a blood transfusion.
- Exchange Transfusion: In rare cases, when bilirubin levels are dangerously high, an exchange transfusion may be performed to quickly remove bilirubin from the baby’s blood.
Phototherapy is a safe and effective treatment for managing jaundice in newborns. Babies typically respond well and recover quickly. If your baby requires phototherapy, make sure to follow all instructions provided by your healthcare team and continue monitoring your baby’s feeding and behavior at home.
Newborn Jaundice – Discharge and Aftercare
Once your baby’s bilirubin levels have dropped to a safe range, they will be discharged from the hospital. However, even after discharge, it’s important to continue monitoring your baby for any signs of recurring jaundice.
Key Considerations After Discharge:
- Follow-Up Appointments: Your pediatrician will likely schedule follow-up appointments to ensure that your baby’s bilirubin levels are remaining low.
- Watch for Recurrence: In some cases, jaundice may return after treatment, especially if your baby isn’t feeding well or is dehydrated.
- Continue Feeding Frequently: Keep feeding your baby frequently to maintain their hydration and help eliminate any remaining bilirubin.
Using tools like our Baby Health Monitor to track your baby’s recovery and Digital Baby Scale to monitor weight gain will help you stay proactive in your baby’s care.
Managing Jaundice in Newborns at Home After Discharge

Even after your baby is discharged, it’s crucial to continue practicing the same techniques at home to ensure that jaundice doesn’t return. This means maintaining regular feedings, tracking your baby’s progress, and scheduling follow-up appointments as needed. If your baby had a more severe case of jaundice, your pediatrician will provide a detailed aftercare plan.
With proper attention and care, managing jaundice in newborns at home becomes much easier. Having the right tools to monitor your baby’s health will give you peace of mind and allow you to keep track of their recovery.
Recap: Jaundice – Management of Neonatal Jaundice
Jaundice in newborns can be a worrying experience for parents, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can be managed effectively. Whether your baby needs simple home care or medical treatments like phototherapy, understanding the condition and knowing how to respond is essential. By using products like our Breastfeeding Pillow, Digital Baby Scale, and Baby Health Monitor, you can ensure your baby’s recovery and health is well supported.
Managing jaundice in newborns doesn’t have to be overwhelming, especially with proper care, consistent feeding, and monitoring. Most cases resolve within a few weeks, and with the right precautions, your baby will be back to full health in no time

